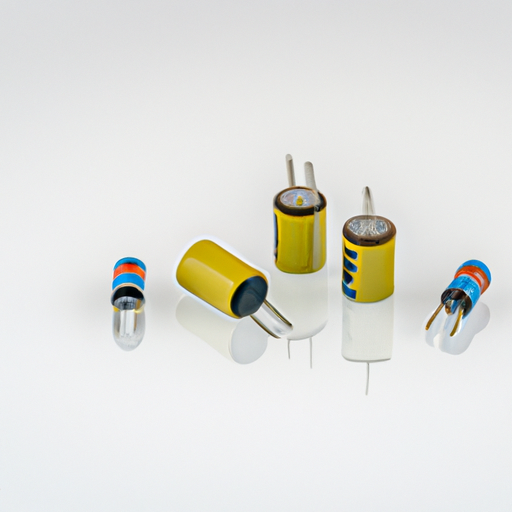
Important Product Categories of Capacitors Manufacturers
I. Introduction
Capacitors are fundamental components in the world of electronics, serving as energy storage devices that can release energy quickly when needed. They play a crucial role in various applications, from smoothing out voltage fluctuations in power supplies to enabling signal processing in communication devices. The capacitor manufacturing industry has evolved significantly over the years, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing demand for more efficient and compact electronic devices. This blog post will explore the important product categories of capacitors manufacturers, highlighting their characteristics, applications, and emerging trends.
II. Types of Capacitors
A. Electrolytic Capacitors
Electrolytic capacitors are polarized capacitors that use an electrolyte to achieve a larger capacitance per unit volume. They are widely used in power supply circuits, audio equipment, and various consumer electronics due to their high capacitance values.
**Characteristics and Applications:** Electrolytic capacitors typically have capacitance values ranging from microfarads (µF) to several thousand microfarads, making them ideal for applications requiring significant energy storage. They are often used in power supply filters, coupling and decoupling applications, and audio signal processing.
**Advantages and Disadvantages:** The primary advantage of electrolytic capacitors is their high capacitance-to-volume ratio. However, they have a limited lifespan, are sensitive to temperature and voltage, and can fail if subjected to reverse polarity.
B. Ceramic Capacitors
Ceramic capacitors are non-polarized capacitors made from ceramic materials. They are available in two main classes: Class 1 (temperature stable) and Class 2 (high capacitance).
**Types (Class 1 and Class 2):** Class 1 capacitors are known for their stability and low loss, making them suitable for precision applications. Class 2 capacitors, on the other hand, offer higher capacitance values but with less stability.
**Applications and Benefits:** Ceramic capacitors are commonly used in high-frequency applications, decoupling, and filtering. Their small size and reliability make them a popular choice in consumer electronics, automotive, and telecommunications.
C. Film Capacitors
Film capacitors are made from thin plastic films as the dielectric material. They are known for their stability, low loss, and excellent performance in high-frequency applications.
**Types (Polyester, Polypropylene, etc.):** Different types of film capacitors include polyester, polypropylene, and polycarbonate, each with unique properties suited for specific applications.
**Key Applications and Features:** Film capacitors are widely used in audio equipment, power electronics, and motor run applications. Their ability to handle high voltages and currents makes them suitable for demanding environments.
D. Tantalum Capacitors
Tantalum capacitors are another type of electrolytic capacitor, but they use tantalum metal as the anode. They are known for their reliability and stability.
**Properties and Uses:** Tantalum capacitors offer high capacitance in a small package and are often used in applications where space is limited, such as in mobile devices and military equipment.
**Comparison with Other Types:** Compared to aluminum electrolytic capacitors, tantalum capacitors have a lower equivalent series resistance (ESR) and better performance at high frequencies, but they are generally more expensive.
E. Supercapacitors
Supercapacitors, also known as ultracapacitors, are energy storage devices that bridge the gap between traditional capacitors and batteries. They can store a large amount of energy and release it quickly.
**Definition and Working Principle:** Supercapacitors store energy through electrostatic charge separation, allowing them to charge and discharge rapidly.
**Applications in Energy Storage:** They are used in applications requiring quick bursts of energy, such as in regenerative braking systems in electric vehicles, backup power supplies, and energy harvesting systems.
F. Mica Capacitors
Mica capacitors are known for their high stability and low loss, making them ideal for high-frequency applications.
**Characteristics and Applications:** They are often used in RF applications, oscillators, and timing circuits due to their excellent performance in extreme conditions.
**Advantages in High-Frequency Applications:** Mica capacitors have a very low dielectric loss, making them suitable for applications where signal integrity is critical.
III. Specialized Capacitors
A. Power Capacitors
Power capacitors are designed to improve the power factor in electrical systems, helping to reduce energy losses and improve efficiency.
**Role in Power Factor Correction:** They are commonly used in industrial settings to correct power factor issues caused by inductive loads, such as motors and transformers.
**Applications in Industrial Settings:** Power capacitors are essential in substations, manufacturing plants, and commercial buildings to enhance the overall efficiency of electrical systems.
B. RF Capacitors
RF capacitors are specialized capacitors designed for radio frequency applications, where performance at high frequencies is critical.
**Importance in Radio Frequency Applications:** They are used in RF amplifiers, filters, and oscillators, where maintaining signal integrity is paramount.
**Key Specifications and Uses:** RF capacitors must have low ESR and high self-resonant frequency to perform effectively in RF circuits.
C. High Voltage Capacitors
High voltage capacitors are designed to operate at voltages significantly higher than standard capacitors, making them essential in power transmission and distribution systems.
**Applications in Power Transmission:** They are used in substations, power plants, and high-voltage transmission lines to manage voltage levels and improve system stability.
**Design Considerations and Challenges:** Designing high voltage capacitors involves addressing issues such as dielectric breakdown, thermal management, and physical size constraints.
D. Automotive Capacitors
With the rise of electric vehicles and advanced automotive electronics, automotive capacitors have become increasingly important.
**Role in Modern Vehicles:** They are used in various applications, including power management, infotainment systems, and safety features.
**Trends in Automotive Electronics:** The shift towards electric and hybrid vehicles is driving demand for capacitors that can handle higher voltages and provide reliable performance in harsh environments.
IV. Emerging Trends in Capacitor Manufacturing
A. Miniaturization and High-Density Capacitors
As electronic devices become smaller and more compact, the demand for miniaturized capacitors has increased.
**Impact on Electronic Design:** High-density capacitors allow for more efficient use of space in circuit boards, enabling the development of smaller and more powerful devices.
**Challenges in Manufacturing:** The miniaturization of capacitors presents challenges in terms of maintaining performance, reliability, and manufacturability.
B. Environmentally Friendly Capacitors
There is a growing trend towards the development of environmentally friendly capacitors that use sustainable materials and manufacturing processes.
**Shift Towards Sustainable Materials:** Manufacturers are exploring alternatives to traditional materials that may have negative environmental impacts, such as lead and other hazardous substances.
**Regulatory Influences:** Increasing regulations regarding electronic waste and environmental sustainability are driving the adoption of greener capacitor technologies.
C. Smart Capacitors
The integration of capacitors with IoT and smart devices is an emerging trend that promises to enhance the functionality of electronic systems.
**Integration with IoT and Smart Devices:** Smart capacitors can provide real-time monitoring and control, improving energy efficiency and performance in various applications.
**Future Potential and Applications:** As the demand for smart technologies continues to grow, the role of capacitors in these systems will become increasingly important.
V. Conclusion
In summary, capacitors are essential components in the electronics industry, with various types and specialized categories serving different applications. Understanding the characteristics and uses of different capacitor types is crucial for manufacturers and consumers alike. As the capacitor manufacturing industry continues to evolve, emerging trends such as miniaturization, environmentally friendly materials, and smart technologies will shape the future of capacitors, ensuring their relevance in an ever-changing technological landscape.
VI. References
- Academic journals and articles on capacitor technology and applications.
- Industry reports and market analysis on the capacitor manufacturing sector.
- Manufacturer websites and product catalogs for detailed specifications and product offerings.
This comprehensive overview of the important product categories of capacitors manufacturers highlights the diversity and significance of capacitors in modern electronics, providing valuable insights for industry professionals and enthusiasts alike.